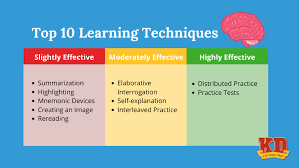
Studying effectively is not just about spending long hours with books. It is about using the right strategies, managing your time well, and understanding how learning actually works. Many students work hard but still struggle to achieve the results they want because they rely on ineffective methods, such as rereading notes or cramming the night before exams. Effective studying means working smarter, not harder. This article explains the best techniques that students can use to learn faster, retain information longer, and perform better in their exams and daily academic life.
Understand How Learning Works
Before applying any study techniques, it is essential to understand how the brain learns. Learning happens when you actively engage with information. This means you need to think about it, recall it, apply it, or teach it to someone else. Passive learning, such as simply reading or listening, does not help your brain form strong memories. Effective studying focuses on active learning strategies.
1. Use Active Recall
Active recall is one of the most powerful and scientifically proven study techniques. It involves testing yourself repeatedly instead of just reading notes. When you try to remember information without looking at your books, your brain strengthens the memory pathway.
How to use active recall:
- After reading a chapter, close the book and try to summarize it from memory.
- Use flashcards to quiz yourself.
- Solve practice questions without checking the answers first.
- Teach the lesson to someone else or pretend to teach it aloud.
This technique forces the brain to retrieve information, which improves long-term memory and helps you understand concepts deeply.
2. Apply Spaced Repetition
Spaced repetition means reviewing information at increasing intervals over time instead of cramming everything in one night. Research shows that the brain remembers information much better when it is reviewed repeatedly with breaks in between.
Example spacing schedule:
- First review: the same day you learn something
- Second review: after 24 hours
- Third review: after 3 days
- Fourth review: after 1 week
- Fifth review: after 1 month
Using spaced repetition helps you remember information for exams and even long after the course ends. You can use flashcard apps like Anki or Quizlet, or simply follow your own review schedule.
3. Follow the Pomodoro Technique
The Pomodoro Technique is a time-management method that helps you stay focused and avoid burnout. It breaks your study time into short, productive intervals with scheduled breaks.
Follow these steps:
- Choose a task to study.
- Set a timer for 25 minutes and study with full concentration.
- Take a 5-minute break.
- After four cycles, take a longer break of 15 to 30 minutes.
This technique keeps your mind fresh, prevents distractions, and increases productivity.
4. Make a Study Schedule
A written study plan helps you organize your time and reduce stress. Many students waste hours deciding what to study each day. A schedule removes confusion and gives you a clear structure.
Tips for making an effective study schedule:
- Identify your subjects and weekly goals.
- Break large tasks into smaller, manageable pieces.
- Allocate specific times for studying each subject.
- Review your schedule weekly and adjust as needed.
A study schedule not only saves time but also creates a habit of consistency, which is essential for academic success.
5. Create a Distraction-Free Study Environment
Your study environment plays a major role in how well you perform. A messy, noisy, or chaotic setting can reduce concentration and waste valuable time.
To create a productive study environment:
- Choose a quiet, well-lit place.
- Keep your desk clean and clutter-free.
- Turn off unnecessary notifications on your phone.
- Keep all required materials within reach.
A calm and organized study space helps your brain focus better and increases the quality of your learning.
6. Use the Feynman Technique
The Feynman Technique is a powerful method for understanding complex concepts. It involves explaining a topic in simple words as if you are teaching it to a child.
Steps of the Feynman Technique:
- Choose a concept you want to learn.
- Write a simple explanation of it without using complicated vocabulary.
- Identify the areas you cannot explain clearly.
- Return to your study material and learn those parts again.
- Simplify your explanation further until it becomes easy and logical.
This technique exposes gaps in your understanding and strengthens your knowledge.
7. Break Information into Chunks
The brain remembers information better when it is divided into small, meaningful chunks rather than long paragraphs. This method is known as chunking.
Example:
Instead of memorizing a long list of points, group related ideas together. This makes learning easier and helps improve clarity.
8. Take Effective Notes
Good notes act as a personal guide for revision. They save time and help you understand lessons faster.
Tips for taking better notes:
- Do not write everything word for word.
- Use headings, subheadings, bullet points, and diagrams.
- Highlight key concepts or formulas.
- Rewrite difficult notes in your own words.
Effective notes make revision easier and help you retain information longer.
9. Use Multiple Learning Methods
Everyone has different learning preferences. Using various methods keeps studying interesting and improves understanding.
Examples of different learning methods:
- Reading and summarizing
- Watching educational videos
- Listening to audio lectures
- Practicing diagrams and flowcharts
- Solving past papers
- Discussing topics with classmates
Combining methods helps you learn from different angles and strengthens your overall understanding.
10. Stay Healthy for Better Learning
Good physical and mental health directly affect your ability to learn. A tired or stressed brain cannot absorb information effectively.
Healthy habits that support learning:
- Get 7 to 8 hours of sleep daily.
- Eat balanced meals and drink enough water.
- Exercise regularly to improve concentration.
- Take short breaks during study sessions.
- Avoid studying late at night if possible.
A healthy body supports a sharp and active mind.
11. Review Your Progress Regularly
Many students study but never check whether their methods are working. Reviewing your progress helps you identify weaknesses and adjust your strategies.
Ask yourself:
- What subjects am I improving in?
- Where am I still struggling?
- Are my study methods effective?
- What can I change to perform better?
Self-evaluation helps you become a smarter learner and keeps you on track.
12. Avoid Cramming
Cramming may help you pass one test, but it does not create long-term understanding. Information learned through cramming is easily forgotten. Effective learning requires regular practice and deep understanding of concepts.
Conclusion
Studying effectively is a combination of smart techniques, consistent habits, and a positive mindset. Strategies like active recall, spaced repetition, the Pomodoro Technique, and good note-taking can transform your academic performance. By building a study schedule, managing your environment, and maintaining your health, you can study more efficiently and achieve better results. Remember, you do not need long hours of studying to succeed; you need the right methods. When you focus on understanding instead of memorizing, and consistency instead of cramming, you become a confident and successful learner.